DNA & Protein Synthesis Chapter 8
What exactly is DNA and why is it considered the carrier of our genetic makeup?
What is DNA and where does it come from?
Identifying DNA as the carrier of genetic material Section 8.1
How did we figure this out????
Griffith's experiment reported in 1928 shows that bacteria have the ability to transfer "something"....
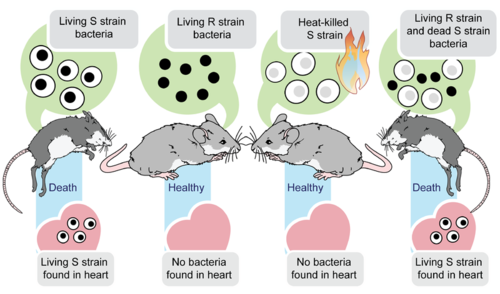
Griffith Avery Experiment

Hershey Chase Experiment
Structure of DNA 8.2
Deoxyribonucleic Acid aka DNA has a very unique structure identified as a DOUBLE HELIX.
DNA is composed of a Sugar-Phosphate-Sugar-Phosphate-Sugar-Phosphate backbone (represented as the blue and red line)......

Each DNA molecule is composed of many subunits (monomers) known as a NUCLEOTIDES that hold the 2 strands together.
It is composed of a Phosphate group, Sugar, and a Base

DNA has 4 nitrogenous bases known as Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) that make up DNA's structure.
Each one has its unique structure and is the complimentary pair to another. They are bonded together by the help of HYDROGEN BONDS

Scientists Credited for DNA Discovers Include....
Rosalind Franklin who discovered the image of DNA using X-rays.

Watson and Crick who discovered the structure of DNA using Rosalind Franklin's work in 1953.

Watson Explains Base Pairing
Match Up These Pairs With Their Corresponding Base Pair....
ATT GCG TAC GAT CGA TGC AGC AAA GCA

DNA Replication 8.3
Where does this occur?
When does this occur?
DNA molecule is read 3' (Three Prime) to 5' (Five Prime)
What is that???? DNA double helix is written ANTI-PARALLEL



Overview

DNA replicates in a few steps but many proteins are involved. Lets focus on a couple....
Step 1: DNA is unzipped at multiple sites of the strand by enzymes known as Helicase

Step 2: Another enzyme called DNA Polymerase begins creating the DNA new strand by pairing A-T and G-C.
The new strand is copied 3' to 5'

Step 3: 2 Identical copies of DNA are created.

DNA Replication
Amoeba Sisters Replication
Segments (pieces) of DNA code are known as GENES and MANY GENES together make up a CHROMOSOME
So....what are Genes????
Analogy:
DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes can be compared to parts of a book....
 A book is like the
A book is like the 
 A Chapter is like the
A Chapter is like the 
 Words are like the
Words are like the 
Summary

What is DNA and where does it come from?
Identifying DNA as the carrier of genetic material Section 8.1
How did we figure this out????
Griffith's experiment reported in 1928 shows that bacteria have the ability to transfer "something"....

Griffith Avery Experiment
Hershey Chase Experiment
Structure of DNA 8.2
Deoxyribonucleic Acid aka DNA has a very unique structure identified as a DOUBLE HELIX.
DNA is composed of a Sugar-Phosphate-Sugar-Phosphate-Sugar-Phosphate backbone (represented as the blue and red line)......
Each DNA molecule is composed of many subunits (monomers) known as a NUCLEOTIDES that hold the 2 strands together.
It is composed of a Phosphate group, Sugar, and a Base
DNA has 4 nitrogenous bases known as Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) that make up DNA's structure.
Each one has its unique structure and is the complimentary pair to another. They are bonded together by the help of HYDROGEN BONDS
Scientists Credited for DNA Discovers Include....
Rosalind Franklin who discovered the image of DNA using X-rays.

Watson and Crick who discovered the structure of DNA using Rosalind Franklin's work in 1953.
Watson Explains Base Pairing
Match Up These Pairs With Their Corresponding Base Pair....
ATT GCG TAC GAT CGA TGC AGC AAA GCA
DNA Replication 8.3
Where does this occur?
When does this occur?
DNA molecule is read 3' (Three Prime) to 5' (Five Prime)
What is that???? DNA double helix is written ANTI-PARALLEL
Overview

DNA replicates in a few steps but many proteins are involved. Lets focus on a couple....
Step 1: DNA is unzipped at multiple sites of the strand by enzymes known as Helicase
Step 2: Another enzyme called DNA Polymerase begins creating the DNA new strand by pairing A-T and G-C.
The new strand is copied 3' to 5'
Step 3: 2 Identical copies of DNA are created.

DNA Replication
Amoeba Sisters Replication
Segments (pieces) of DNA code are known as GENES and MANY GENES together make up a CHROMOSOME
So....what are Genes????
Analogy:
DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes can be compared to parts of a book....
Summary