Viruses

 Above is the picture of the flu virus or Influenza. on the left and HIV on the right.
Above is the picture of the flu virus or Influenza. on the left and HIV on the right.
Any living organism or particle that causes diseases are known as pathogens.
A virus is an infectious particle only composed of a protein coat and genetic material (nucleic acid).
 Lock and Key Mechanism
Lock and Key Mechanism
They don't even have a place in the Linnaean Classification System.

How do they reproduce?
Viruses can not reproduce on their own. They must use the host's cell to replicate.
Lytic Cycle: Infectious pathway where the host cell lyses (bursts) releasing new viral offspring into the host.
Lysogenic Cycle: Infectious pathway where the virus integrates (combines) its nucleic acid with the hosts DNA.
The host cells replicates and along with each new cell the virus nucleic acid replicates with it......waiting for something to trigger the production of new viruses.


HIV is a retrovirus!! Retroviruses contain RNA. In order to replicate they must use the host's machinery to create DNA from RNA.....?..... using this is the process
RNA --> DNA --> RNA --> Proteins
This extra step (RNA to DNA) is a major reason why these viruses are harder to treat. This leads to more chances of mutations and harder to treat. Also retroviruses genetic material can remain integrated in the hosts DNA for long periods of time before it becomes active again.

Some organisms are immune to HIV because they lack the CD4 Protein Receptors!!!
They even infect bacteria!
These viruses are known as Bacteriophages
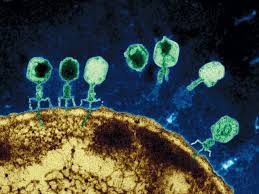

Viruses that infect plants are known as Viroids.



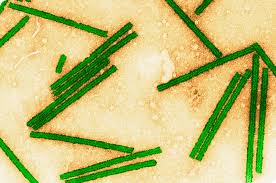
Prions are infectious protein particles that affect proteins (EX: Madcow-affect the brain)


Flu Virus Attack
Benefits
Scientist use weak strands of viruses to come up with VACCINES
Diseases associated with Viruses
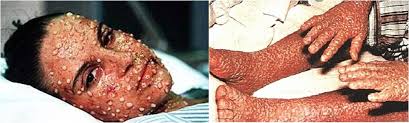 Smallpox
Smallpox 
 Mumps Virus
Mumps Virus

 HPV
HPV 

 HIV
HIV 

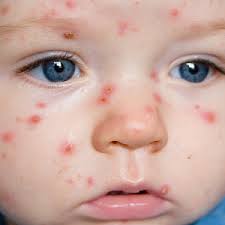 Chickenpox Virus
Chickenpox Virus

 Ebola Virus
Ebola Virus


 Polio Virus
Polio Virus 
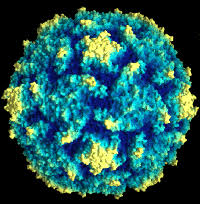
 Rabies Virus
Rabies Virus 

Rabies In Humans
Chp 18.1 &18.2 Quiz
Prokaryotes
Characteristics:
- no membrane bound organelles
- free floating DNA in circular form and/or a plasmid (separate part of DNA)
- unicellular
- motile (movement) by use of flagella and/or pili

Groups of Prokaryotes
- Obligate anaerobes can not survive in the presence of O2
- Obligate aerobes must have O2 to survive
- Facultative aerobes are can survive in the presence or absence of O2.
Archaebacteria vary in shapes and live in extreme environments
There are 3 types of structures of Eubacteria.
Rod shape - Bacilli
Spiral shape - Spirilla
Spherical shape - Cocci
Reproduction/Conjugation
Bacteria reproduce sexually using their pili

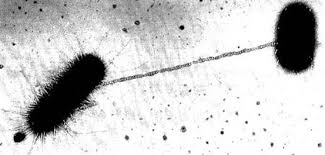
They can also reproduce asexually through BINARY FISSION.

Gram Staining

Gram Negative Bacteria have the extra layer of protection which makes them harder to treat. Their cell walls are resistant to several classes of antibiotics.

Benefits/Treatments
Some bacteria inside our bodies are beneficial. They help organisms breakdown food. Some make vitamins and other compounds.
They have a mutualistic symbiosis with organisms. Bacteria breakdown food and keep them healthy, while organisms protect them.
Bacteria can be treated with Antibiotics.
Brainpop
Amoeba Sister's Prokaryotes Review

EXAMPLES
E.coli & Salmonella= cause food poisoning


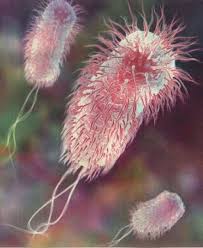
H.Pylori= cause ulcers and gastritis


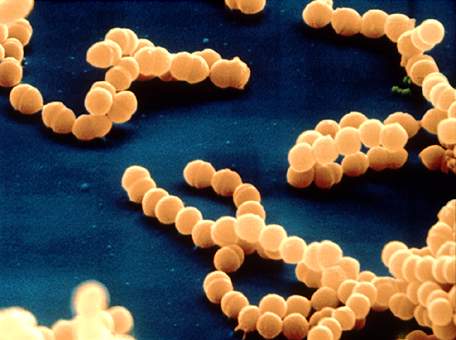
Staphylococcus aureus= causes a variety of infections in the body, including boils, cellulitis, abscesses, wound infections, toxic shock syndrome, pneumonia, and food poisoning
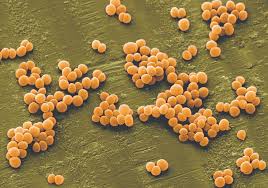
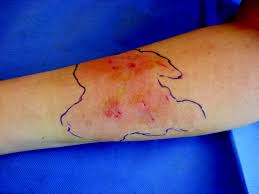
Streptococcus pyogenes = strept throat

Nactrotizing fasciitis = Flesh eating bacteria


Bringing Awareness To A Pathogen
Above is the picture of the flu virus or Influenza. on the left and HIV on the right.
Any living organism or particle that causes diseases are known as pathogens.
A virus is an infectious particle only composed of a protein coat and genetic material (nucleic acid).
They don't even have a place in the Linnaean Classification System.

How do they reproduce?
Viruses can not reproduce on their own. They must use the host's cell to replicate.
Lytic Cycle: Infectious pathway where the host cell lyses (bursts) releasing new viral offspring into the host.
Lysogenic Cycle: Infectious pathway where the virus integrates (combines) its nucleic acid with the hosts DNA.
The host cells replicates and along with each new cell the virus nucleic acid replicates with it......waiting for something to trigger the production of new viruses.
HIV is a retrovirus!! Retroviruses contain RNA. In order to replicate they must use the host's machinery to create DNA from RNA.....?..... using this is the process
RNA --> DNA --> RNA --> Proteins
This extra step (RNA to DNA) is a major reason why these viruses are harder to treat. This leads to more chances of mutations and harder to treat. Also retroviruses genetic material can remain integrated in the hosts DNA for long periods of time before it becomes active again.
Some organisms are immune to HIV because they lack the CD4 Protein Receptors!!!
They even infect bacteria!
These viruses are known as Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect plants are known as Viroids.
Prions are infectious protein particles that affect proteins (EX: Madcow-affect the brain)
Flu Virus Attack
Benefits
Scientist use weak strands of viruses to come up with VACCINES
Diseases associated with Viruses
 Polio Virus
Polio Virus 
Rabies In Humans
Chp 18.1 &18.2 Quiz
Prokaryotes
Characteristics:
- no membrane bound organelles
- free floating DNA in circular form and/or a plasmid (separate part of DNA)
- unicellular
- motile (movement) by use of flagella and/or pili
Groups of Prokaryotes
- Obligate anaerobes can not survive in the presence of O2
- Obligate aerobes must have O2 to survive
- Facultative aerobes are can survive in the presence or absence of O2.
Archaebacteria vary in shapes and live in extreme environments
There are 3 types of structures of Eubacteria.
Rod shape - Bacilli
Spiral shape - Spirilla
Spherical shape - Cocci
Reproduction/Conjugation
Bacteria reproduce sexually using their pili

They can also reproduce asexually through BINARY FISSION.
Gram Staining
Gram Negative Bacteria have the extra layer of protection which makes them harder to treat. Their cell walls are resistant to several classes of antibiotics.
Benefits/Treatments
Some bacteria inside our bodies are beneficial. They help organisms breakdown food. Some make vitamins and other compounds.
They have a mutualistic symbiosis with organisms. Bacteria breakdown food and keep them healthy, while organisms protect them.
Bacteria can be treated with Antibiotics.
Brainpop
Amoeba Sister's Prokaryotes Review
EXAMPLES
E.coli & Salmonella= cause food poisoning
H.Pylori= cause ulcers and gastritis

Staphylococcus aureus= causes a variety of infections in the body, including boils, cellulitis, abscesses, wound infections, toxic shock syndrome, pneumonia, and food poisoning
Streptococcus pyogenes = strept throat

Nactrotizing fasciitis = Flesh eating bacteria
Bringing Awareness To A Pathogen