If you cut your finger, your cells grow and divide to make more cells. This is how your finger heals.
Cells grow and divide in a regular pattern, or cycle that is referred to as the .....
The Cell Cycle 5.1
Cells grow and divide in a regular pattern, or cycle that is referred to as the .....
The Cell Cycle 5.1
The cell cycle has 4 main stages:
Gap 1 (G1): During this stage the cell grows in size and organelles get replicated. The cell spends 8-10 hrs in this stage (most of its time is spent here).
Synthesis (S): During this stage the cell synthesizes (makes) duplicate copies of its DNA. The cell spends 6-8 hrs in this stage.
Gap 2 (G2): During this stage the cell checks for errors in DNA synthesis and begins to grow in size preparing itself for cellular division. The cell spends 4-6 hrs in this stage.
These Three Stages Are Known As Interphase

Mitosis (Mitotic Phase) (M): During this stage the cell prepares to divides into two cells through the process of Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase. The cell spends 3 hrs to complete this stage.
Cytokinesis is the process of the cell completely dividing into two cells.
Lets assess your knowledge....Quiz On HMH account, LOG IN
Section 5.2 The Stages of Mitosis:
Your nucleus commands cells to divide but before it divides it must first duplicate and condense its DNA into CHROMOSOMES.....
If you stretched the DNA in one cell all the way out, it
would be about 2m long and all the DNA in all your cells
put together would be about twice the diameter of the
Solar System.
DNA Condensing Video
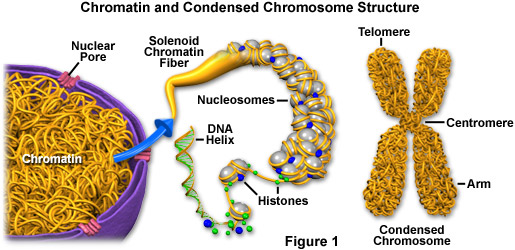
Lets understand the structure of a chromosome (condensed form of DNA)....
Chromosome Structure:
- A chromosome is one long continuous thread of DNA.
- DNA wraps around proteins called histones.
- DNA and histones form chromatin, which looks like spaghetti, during interphase.
- Chromosomes condense tightly for mitosis
because they are duplicated, they look like an X.
Lets examine the phases of cellular division known as Mitosis....
Lets examine the phases of cellular division known as Mitosis....

1. interphase: copies DNA, grows, duplicates organelles
2. prophase: chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope
breaks down, spindle fibers form
3. metaphase: spindle fibers align chromosomes along the
cell equator
4. anaphase:
chromatids separate to opposite sides of cell
6. cytokinesis: divides the cytoplasm between two
daughter cells
Prophase:
Metaphase:

Anaphase:

Telophase:
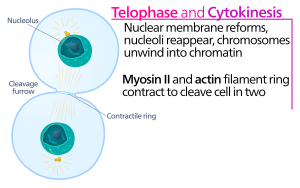
Cytokinesis:

BrainPop Mitosis Video
Lets assess your knowledge....
Mitosis Dance
Section 5.3 Regulation of Cells:
If the cell goes out of control, cancer can result. Cancer is uncontrolled/unregulated cell division.
Just as cells need to grow and divide, other cells need to
die. Internal or external signals can start an orderly
process of cell death. The cell is broken down and its
parts are reused in building other molecules. This
process of programmed cell death is called apoptosis
Apoptosis Video

Cancer Animation
Section 5.4 Asexual Reproduction:

Advantages of Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction:
Quick
One parent needed
All good characteristics are passed on
Disadvantages:
No variation (all look the same)
Offspring inherit bad traits
Adaptation to environment is unlikely
Section 5.5 Multicellular Life:
Cell differentiation- not all cells look alike
or perform the same function but at one
point they all had a choice.
What Are Stem Cells?