Chemical Energy and ATP Section 4.1
The cells of all organisms-from algae to whales to people- need chemical energy for all their processes.
Some organisms absorb energy from sunlight that is stored in sugars called photosynthesis.
But where do you get this kind of energy? From food? What kind of biomolecules help you achieve energy?
All organisms use this energy known as adenosine triphosphate or ATP. Cells use ATP for functions such as moving material across a membrane by active transport.

The energy found in ATP, a high energy molecule, is released when the third phosphate is removed converting it to ADP, a low energy molecule (adenosine diphosphate)

What types of biomolecules provide us with energy?
Carbohydrates
• molecules most commonly broken down
• glucose yields about 36 ATP
• 4 calories per mg (4 Calories per gram)
Lipids
• triglyceride yields about 146 ATP
• molecules that store most of the energy in a person’s body
• 9 calories per mg (9 Calories per gram)
Proteins
• molecules least likely to be broken down
• store about the same amount of energy as carbohydrates
• 9 calories 4 calories per mg
(4 Calories per gram)
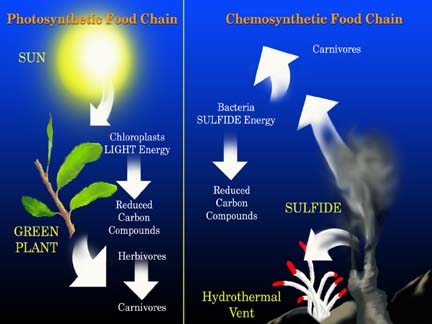
Some organisms use chemicals compounds instead of light energy as their source to make food. This process is known as Chemosynthesis.
Lets assess your knowledge....
Chemical Energy & ATP Quiz
Photosynthesis 4.2

Plants are known as producers because they turn light energy into chemical energy. (they produce their own food)


This happens in a very special organelle of plant cells....
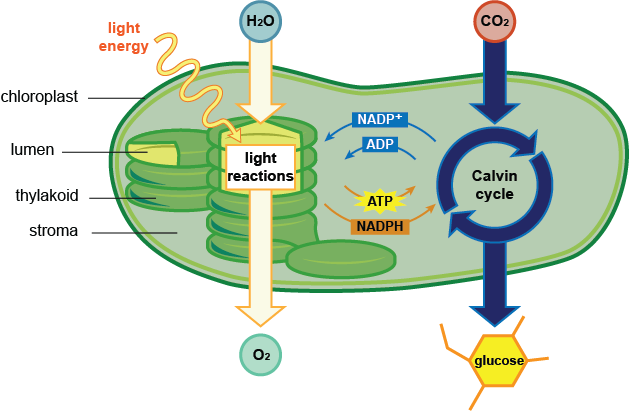
Photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid (light dependent reaction) and stroma (calvin cycle)
Chlorophyll traps visible light and allows for the light
reaction to occur.

Chloroplasts are membrane-bound organelles where photosynthesis takes place in plants.

Photosynthesis takes place in two parts of a chloroplast: the stroma and the granum.
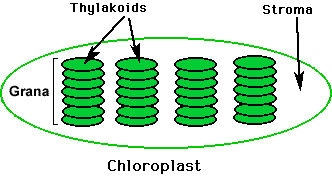
Thylakoids are coin-shaped, membrane-enclosed compartments inside the chloroplast.

Lets assess your knowledge....
Photosynthesis Review Video 1
Photosynthesis Overview Quiz
Cellular Respiration 4.4


Cellular Respiration is known as an aerobic (needs air) process & takes place in 3 parts:
Glycolysis: takes place in the cytoplasm
During this process glucose (sugar) is broken down into 2 molecules known as pyruvate. Pyruvate is a 3 carbon molecule.


Gain 2 ATP per glucose molecule
Inside the Mitochondria 2 reactions take place....
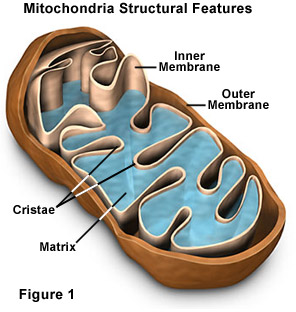
Kreb Cycle (in the matrix of the mitochondria)

Gain 4 ATP per glucose molecule
Electron Transport Chain or ETC (in the inner membrane of the mitochondria)
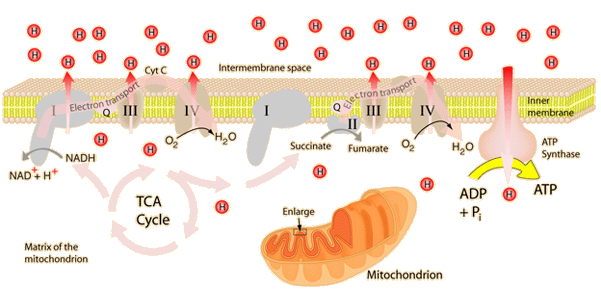
Gain 32 ATP per glucose molecule
In the end Cellular Respiration provides you with ~38 ATP per Glucose molecule

Lets watch CLICK HERE
Your cells can also function temporarily without oxygen....BUT....another route for obtaining ATP must be taken known as FERMENTATION (an anareobic process=no O2 present)

During the process of fermentation your body uses pyruvate to produce lactic acid
Gain 2 ATP in the process (& CO2)
Interesting tip: Yeast go through fermentation but they produce something different....alcohol
The cells of all organisms-from algae to whales to people- need chemical energy for all their processes.
Some organisms absorb energy from sunlight that is stored in sugars called photosynthesis.
But where do you get this kind of energy? From food? What kind of biomolecules help you achieve energy?
All organisms use this energy known as adenosine triphosphate or ATP. Cells use ATP for functions such as moving material across a membrane by active transport.

The energy found in ATP, a high energy molecule, is released when the third phosphate is removed converting it to ADP, a low energy molecule (adenosine diphosphate)

What types of biomolecules provide us with energy?
Carbohydrates
• molecules most commonly broken down
• glucose yields about 36 ATP
• 4 calories per mg (4 Calories per gram)
Lipids
• triglyceride yields about 146 ATP
• molecules that store most of the energy in a person’s body
• 9 calories per mg (9 Calories per gram)
Proteins
• molecules least likely to be broken down
• store about the same amount of energy as carbohydrates
• 9 calories 4 calories per mg
(4 Calories per gram)
Some organisms use chemicals compounds instead of light energy as their source to make food. This process is known as Chemosynthesis.

Lets assess your knowledge....
Chemical Energy & ATP Quiz
Photosynthesis 4.2
Plants are known as producers because they turn light energy into chemical energy. (they produce their own food)


This happens in a very special organelle of plant cells....

Photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid (light dependent reaction) and stroma (calvin cycle)
Chlorophyll traps visible light and allows for the light
reaction to occur.

Chloroplasts are membrane-bound organelles where photosynthesis takes place in plants.
Photosynthesis takes place in two parts of a chloroplast: the stroma and the granum.

Thylakoids are coin-shaped, membrane-enclosed compartments inside the chloroplast.

Lets assess your knowledge....
Photosynthesis Review Video 1
Photosynthesis Overview Quiz
Cellular Respiration 4.4Cellular Respiration is known as an aerobic (needs air) process & takes place in 3 parts:
Glycolysis: takes place in the cytoplasm
During this process glucose (sugar) is broken down into 2 molecules known as pyruvate. Pyruvate is a 3 carbon molecule.


Gain 2 ATP per glucose molecule
Inside the Mitochondria 2 reactions take place....

Kreb Cycle (in the matrix of the mitochondria)

Gain 4 ATP per glucose molecule
Electron Transport Chain or ETC (in the inner membrane of the mitochondria)

Gain 32 ATP per glucose molecule
In the end Cellular Respiration provides you with ~38 ATP per Glucose molecule

Lets watch CLICK HERE
No comments:
Post a Comment